Artificial Intelligence (AI) has undeniably become all the rage in recent times and it has captivated the attention and imagination of individuals across various domains.
This research piece aims to explore the fascinating world of AI, shedding light on its true nature, its origins, societal impact and the potential for investors to capitalise on this transformative wave.
At a fundamental level, AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to learn, reason and perform tasks with minimal human intervention. It encompasses a broad range of techniques, including machine + deep learning, natural language processing and computer vision. Thus far, AI has demonstrated remarkable capabilities in diverse industries such as finance, healthcare and transportation; and it is rapidly transforming how humans live, work and play. However, it is worth noting that as of now, AI is not a magical entity with human-like consciousness or emotions. AI is ultimately a tool developed by humans, which relies on algorithms and data to make predictions and decisions. So, let us embark on a journey to uncover the remarkable possibilities offered by AI and explore its impact on our lives.
AI - a cluster of related technologies
It is important to understand that “AI” is not any one standalone technology, but rather a group of related technologies.
The term AI is used as a catch-all for software that possesses and seeks to replicate characteristics of human intelligence. Although this might seem like a magic black box, AI systems are essentially just looking for patterns in data and drawing conclusions from them.
To better grasp AI and its investment implications, it will be helpful to first understand how the following key technologies have made AI possible and led to many of the recent breakthroughs in the field.
Machine Learning and Neural Networks
Machine learning algorithms ingest data, learn from it, and then form conclusions informed by that data. Neural networks are a type of machine learning algorithm inspired by the structure and function of neural networks in the human brain. Neural networks are capable of learning from previous experiences and examples, and can adapt their internal parameters to improve performance on specific tasks.
The key to understanding machine learning is that it allows software systems to learn and improve from data, without being explicitly programmed for every possible scenario. Instead of manually coding all the logic, developers provide machine learning algorithms with large amounts of data and let them iteratively optimise their internal models until they achieve satisfactory results on the task at hand. This enables machine learning to solve complex problems that would be extremely difficult or impossible to manually program using traditional software approaches.
For example, when social media platforms X or Facebook determine what should appear in your “feed” or timelines, they are using machine learning to make predictions about the content and posts that will be most relevant to you. Advertisers already use machine learning to optimise the bidding on millions of ad placements every second. It’s used elsewhere in tasks like monitoring customer-service calls, underwriting loans and insurance, detecting fraud, and a bevy of other applications across every industry today.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a powerful form of neural networks. It involves training artificial neural networks with multiple layers (hence "deep") to learn from large amounts of data and perform specific tasks, such as image recognition, natural language processing, or decision-making.
While deep learning has been studied in academic circles for decades, it gained broader attention and adoption in industry after researchers at companies like Google demonstrated its effectiveness in solving complex problems, particularly in the field of artificial intelligence.
Today, deep learning is widely used by various companies and organisations for a range of applications. For example, Google utilises deep learning in its search algorithms, language translation services, and computer vision systems. Salesforce employs deep learning in its CRM platform to analyse customer data and provide insights. IBM's Watson system, which uses deep learning, is deployed in healthcare and retail settings for tasks like diagnosis and customer service. CrowdStrike leverages deep learning in its Falcon platform for advanced cybersecurity threat detection. Finally, companies like Tesla and Waymo heavily lean on deep learning for their self-driving vehicle technologies, enabling tasks such as object detection, path planning, and decision-making.
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an area of artificial intelligence that focuses on understanding, processing, and generating human language. It encompasses a wide range of algorithms and techniques designed to analyse and extract meaning from textual data, such as articles, books, social media posts, and spoken language.
Thanks to the availability of large datasets, powerful computing resources and deep learning models, NLP has made significant advancements in recent years. These advancements have enabled the creation of more accurate and robust language processing systems, leading to improved performance in applications such as chatbots, virtual assistants, language translation services, and sentiment analysis on social media.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large Language Models (LLMs) are powerful deep learning models trained on massive amounts of text data, enabling them to understand and generate human-like language with remarkable coherence.
LLMs such as GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), PaLM, and LaMDA, are autoregressive models that generate text in a sequential manner, predicting each subsequent token based on the previously generated context. This autoregressive property allows LLMs to produce coherent and contextually appropriate language.
LLMs are capable of performing a wide range of language tasks, including text generation, question answering, summarisation, and translation. These models can be adapted to different contexts and domains via a process called “fine-tuning”, which makes these models ever so versatile for various NLP applications.
While LLMs have demonstrated impressive capabilities, there are some well-known limitations. These models can generate biased or misleading outputs (referred to as "hallucinations"), and their lack of true understanding or reasoning abilities means they should be used judiciously and with appropriate oversight.
Nonetheless, LLMs represent a significant milestone in AI research and application, given the success of tools such as OpenAI's ChatGPT, Google's Gemini, and X's Grok. This is a young research area with ongoing investments in research and development, and LLMs can be expected to play an increasingly important role in various industries and applications that rely on natural language processing.
Computer Vision
Computer vision enables machines to perceive and understand visual information from images and videos. It involves techniques such as image recognition, object detection and image segmentation. Computer vision has found applications in various fields including autonomous vehicles, surveillance systems, facial recognition and augmented reality.
The above technologies have collectively played a significant role in advancing AI and enabling the development of intelligent systems that can perceive, understand, reason and interact with the world around them.
AI’s impact on society
AI’s transformative power manifests through its wide array of practical use cases across various industries.
In education, AI is revolutionising personalised learning and adaptive education systems. Nowadays, intelligent tutoring systems leverage AI algorithms to provide individualised instruction and feedback, catering to the unique learning needs of students. AI-powered content recommendation systems suggest relevant learning materials, resources, and courses, enhancing the educational experience and facilitating lifelong learning.
In the field of mobility and transportation, AI is making significant strides. Self-driving cars powered by AI algorithms are being developed and tested, promising safer and more efficient transportation systems. AI-based traffic management systems are optimising traffic flow, reducing congestion and improving overall transportation infrastructure. Furthermore, ride-hailing and ride-sharing platforms are incorporating AI algorithms to optimise driver routing and matching, thereby maximising efficiency and reducing travel times.
AI is also playing a crucial role in addressing environmental challenges. The technology is being used in climate modelling to analyse vast amounts of data and predict climate patterns, aiding in the development of effective mitigation and adaptation strategies. AI-powered energy management systems are optimising energy consumption and reducing waste in buildings, leading to increased energy efficiency and sustainability.
Moreover, AI has found applications in the creative industry, enabling new forms of artistic expression. AI algorithms can now generate music, art, and literature, blurring the boundaries between human creativity and machine-generated content. This opens up exciting possibilities for collaboration between artists and AI systems, pushing the boundaries of imagination and innovation.
AI is also positively impacting other industries. For instance, in healthcare, AI is now assisting in diagnosing diseases, drug development, analysing medical images and developing personalised treatment plans. In finance, AI is automating risk management, fraud detection and trading activities. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are now enhancing customer service by providing instant support and personalised services. Industries like manufacturing are benefiting from AI-driven automation, optimisation of production processes and predictive maintenance. AI is also enhancing cybersecurity by detecting anomalies and preventing cyberattacks. In the entertainment industry, AI now fuels recommendation systems, content creation and virtual reality experiences.
As AI continues to evolve and advance, its impacts are expected to be even more profound. From personalized medicine and smart cities to cybersecurity and space exploration, the potential of AI is vast and ever-expanding.
The challenges and risks
While AI’s potential is vast, this technology is not without challenges and risks that require careful consideration.
The rapid advancement of AI is now raising concerns about the ethical implications and responsible use of this technology. There are ongoing discussions around issues such as bias in AI algorithms, privacy concerns, and the potential for AI to be used maliciously. Additionally, some deeply knowledgeable experts in this field are cautioning that AI poses an existential threat to humanity, highlighting the need for robust safeguards and responsible development to ensure the technology remains beneficial to humanity.
Another concern revolves around the potential displacement of human labour as AI technologies automate tasks previously performed by humans. While this can lead to increased efficiency and productivity, it may also result in job losses and require the workforce to adapt to new roles.
While the probability of such risks materialising is uncertain, it is crucial to address them proactively and establish frameworks that promote transparency, fairness, and the ethical use of AI.
AI - sizing the opportunity
Now that you are familiar with the key AI technologies, in order to conceptualise and frame the AI investment opportunity, it is worth revisiting the previous major technology platform shifts i.e. the adoption of the internet, the advent of the mobile era and cloud computing.
So, without further ado, let us take a trip down memory lane…
You may recall that the internet only became popular in the late 1990s/early 2000s and it enabled global connectivity, facilitated the sharing of data and knowledge, and opened up new avenues for commerce, education, and entertainment.
Only a few years later, in early 2007, former Apple CEO - Steve Jobs stepped onto a stage and unveiled the iPhone. The smartphone took the world by storm, the status quo got disrupted and the era of mobile computing was unleashed. Mobile devices enabled people to access the internet, communicate, and perform various tasks on the go, leading to significant changes in how humans interact, work, and consume information.
In the late 2000s, the cloud revolution (the widespread adoption of cloud computing) began to gain prominence and continues to evolve today. Cloud computing involves the delivery of computing services, such as storage, processing power, and software applications, over the internet. It allows organisations and individuals to access and utilise powerful computing resources without the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure.
The internet, mobile and cloud revolutions not only fostered one of the fastest technological shifts in history; they unleashed the largest wealth-building opportunity in human history! These technologies gave rise to exceptionally successful companies, which created tens of trillions of dollars in shareholder value. Firms like Amazon, Apple, Google, and Microsoft capitalised on these technologies to revolutionise industries, disrupt traditional business models, and create immense wealth for their shareholders. Numerous other companies in ecommerce, online payments, enterprise software also capitalised on these technologies and they collectively created trillions of dollars in shareholder value.
Before the internet and mobile computing, for almost a century, the list of the world’s most valuable companies was perennially dominated by businesses in banking, consumer goods, oil, and industrial conglomerates. Today, less than 25 years after the widespread adoption of the internet, mobile and cloud technologies, seven of the world’s Top 10 largest businesses (as measured by market capitalisation) are technology companies and apart from Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing which is currently valued around US$620 billion, the market capitalisation of each of these technology businesses in this list exceeds US$1 trillion!
If our assessment is correct, after the internet, mobile and cloud computing, AI is the next major platform shift in technology and it has the potential to impact every industry.
AI is still in its early days, but if the viral adoption of generative AI-powered large language models (LLMs) is any indication, this technological revolution has a very long growth runway.
Figure 1 shows OpenAI’s ChatGPT exceeded 100 million monthly active users within its first two months post-launch – the fastest pace of adoption of any application the world has seen to date!
Figure 1: ChatGPT’s meteoric rise!
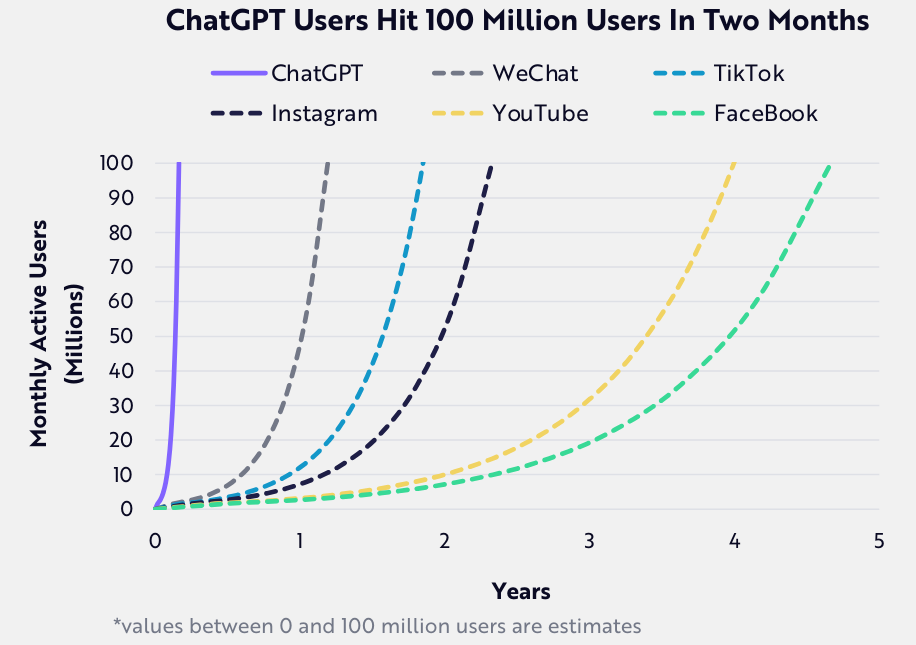
Source: ARK Invest
So far, due to the build out of data centres, the AI megatrend has primarily benefited businesses at the infrastructure layer. The biggest beneficiary has been NVIDIA which currently has more than a 95% market share of specialist AI chips. However, over the past 18 months, investors have also bid up the stocks of the mega-cap technology companies such as Alphabet, Amazon, Meta and Microsoft (which owns a sizeable stake in Open AI).
In these early years of truly useful AI, we believe the key competitive edge for companies will come from accumulating data and having the infrastructure to use AI in their own business (and even provide it to other companies). In AI, data accumulation is crucial because large datasets fuel the accuracy and performance of the AI models. The more diverse and extensive the dataset, the better equipped AI models are to understand nuanced patterns and make accurate predictions. Large datasets enable AI systems to capture a wide range of scenarios, variations and edge cases, allowing them to generalise well and handle real-world complexities. Furthermore, data accumulation facilitates the training and fine-tuning of AI models, enabling continuous improvement and adaptation to changing conditions. In essence, data accumulation is the foundation on which AI algorithms build their understanding of the world, enabling them to deliver meaningful insights, drive innovation, and unlock the full potential of AI across various industries.
Looking to the future, the next steps for AI will be transforming entire industries that have often had limited association with cutting-edge technology. As we noted earlier, self-driving cars are today’s most obvious example of how AI could transform the transportation industry, but this is just a preview of what is to come. It is highly probable that AI will soon be leveraged by nascent industries such as robotics, finance, genomics, the space economy and more.
According to a new report by Bloomberg Intelligence, the generative-AI market is poised to grow revenue by 40% CAGR to approximately US$1.3 trillion by 2032 (Figure 2)!
Figure 2: Generative AI revenue (40% CAGR until 2032)
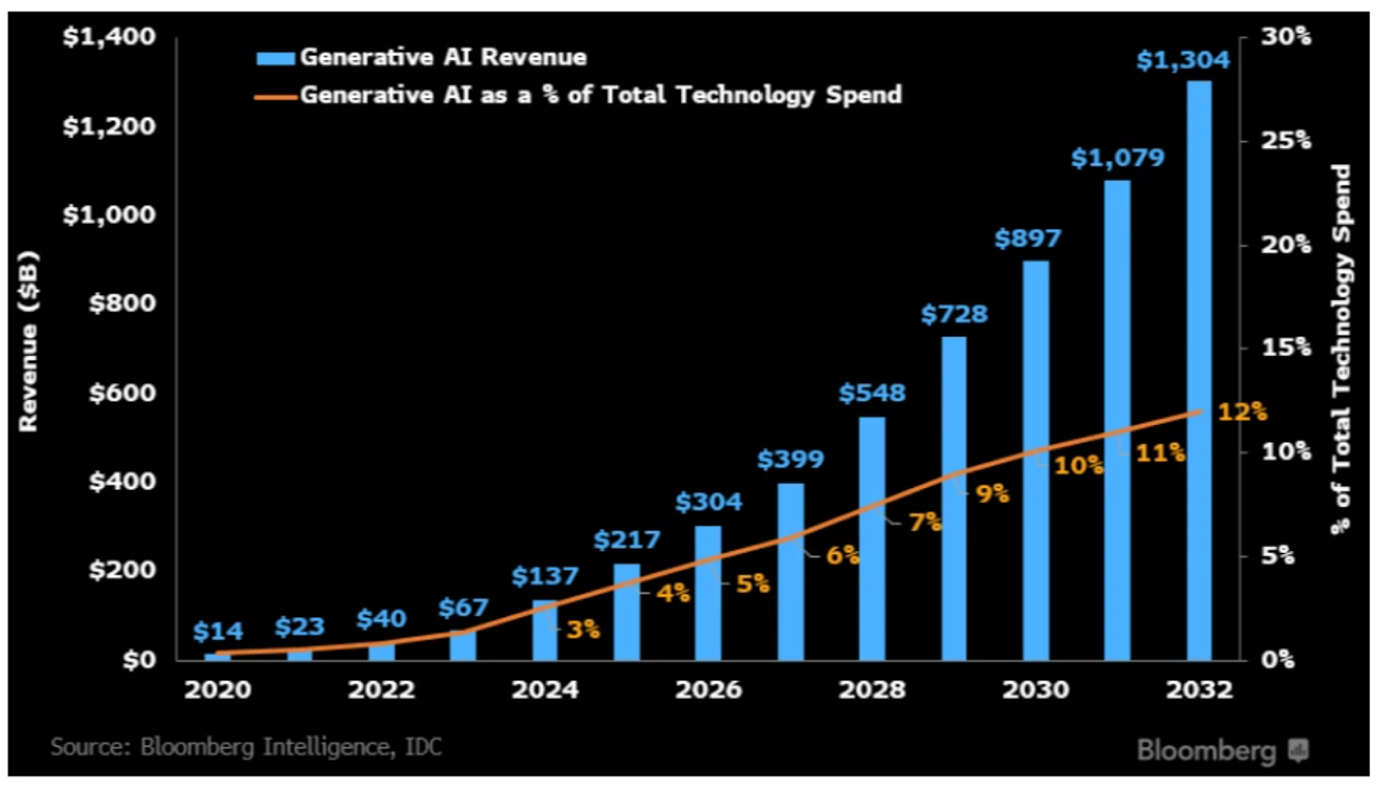
Source: Bloomberg Intelligence
Up until now, the stocks of the “picks and shovels” plays and the mega-cap technology companies have benefited from the AI boom. However, going forwards, we expect companies at the application layer as well as innovative enterprise software companies to deliver outsized gains to investors.
Recently, NVIDIA’s CEO - Jensen Huang summed it up best when he stated that “enterprise software companies are sitting on goldmines and in the future, these AI factories will have their AI agents sitting on top of their software”!
There can be no doubt that some businesses will prosper from the AI revolution but the key for investors will be to separate those businesses that are merely capitalising on hype from those that are building truly useful, scalable, investable AI applications and platforms.
At AlphaTarget, we invest our capital in some of the most promising disruptive businesses at the forefront of secular trends; and utilise stage analysis and other technical tools to continuously monitor our holdings and manage our investment portfolio. AlphaTarget produces cutting-edge research and those who subscribe to our research service gain exclusive access to information such as the holdings in our investment portfolio, our in-depth fundamental and technical analysis of each company, our portfolio management moves and details of our proprietary systematic trend following hedging strategy to reduce portfolio drawdowns. To learn more about our research service, please visit subscriptions.