The e-commerce industry has revolutionised how goods and services are bought and sold, leveraging the power of the internet to create vast marketplaces. It covers a vast range of business activities, from retail and auction websites to business exchanges of goods and services between corporations. E-commerce operates through several core market segments, including business-to-consumer (B2C), business-to-business (B2B), consumer-to-consumer (C2C), and consumer-to-business (C2B).
The e-commerce industry is characterised by its dynamic and rapidly evolving nature, driven by technological advancements and continuously evolving consumer behaviours. Online retailers must navigate various challenges such as digital payment security, logistics networks, omnichannel shopping experiences, and highly competitive market conditions. They must also adapt to changes like the increasing importance of mobile commerce (m-commerce) and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into e-commerce workflows. These technologies enhance personalised shopping experiences, streamline supply chain operations, and optimise customer service, illustrating the industry's quick adoption of innovative solutions to improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Current state of the industry
Over the past 20 years, the e-commerce industry has experienced robust growth and widespread adoption across various global markets. According to Mordor Intelligence, the broader e-commerce market is currently worth an estimated US$8.8 trillion and actual global e-commerce spending will exceed US$6 trillion for the first time this year (Figure 1). It is notable that the global e-commerce market experienced robust growth (27%YoY) during the COVID-19 pandemic, however its growth has moderated over the past 3 years.
This steady growth over the past decade reflects the sustained global preference for online shopping and the increasing integration of technology in commerce operations.
Figure 1: Steady growth in online shopping
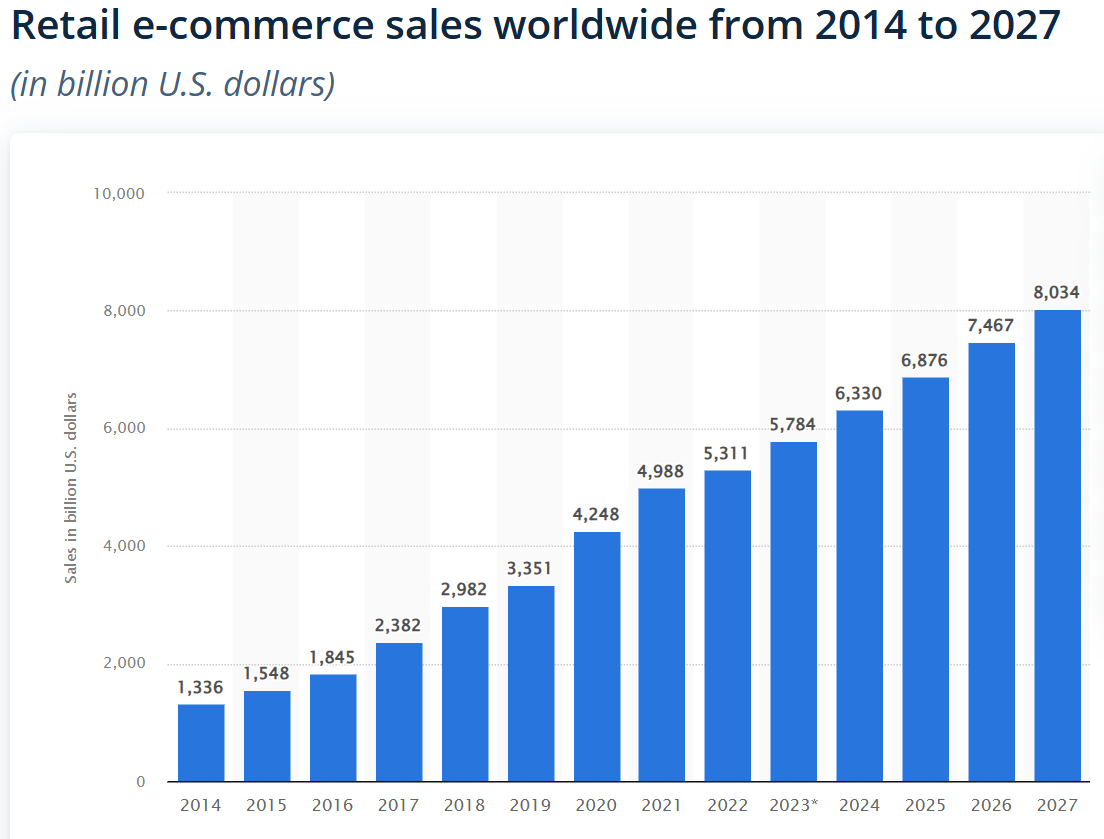
Source: Statista
The Asia Pacific region is the largest market for e-commerce and remarkably China now has a 52% global market share (Figure 2)! After all, Asia is home to approximately 60% of the world’s population and its middle-class is expanding rapidly. Moreover, the continent is experiencing rapid urbanisation and disposable incomes are also rising at a brisk pace. These factors, combined with advancements in mobile technology and more widespread smartphone adoption have made online shopping highly accessible in Asia. Interestingly, e-commerce is growing at an even faster pace in South America where the penetration rates are lower.
Figure 2: Share of the global e-commerce market
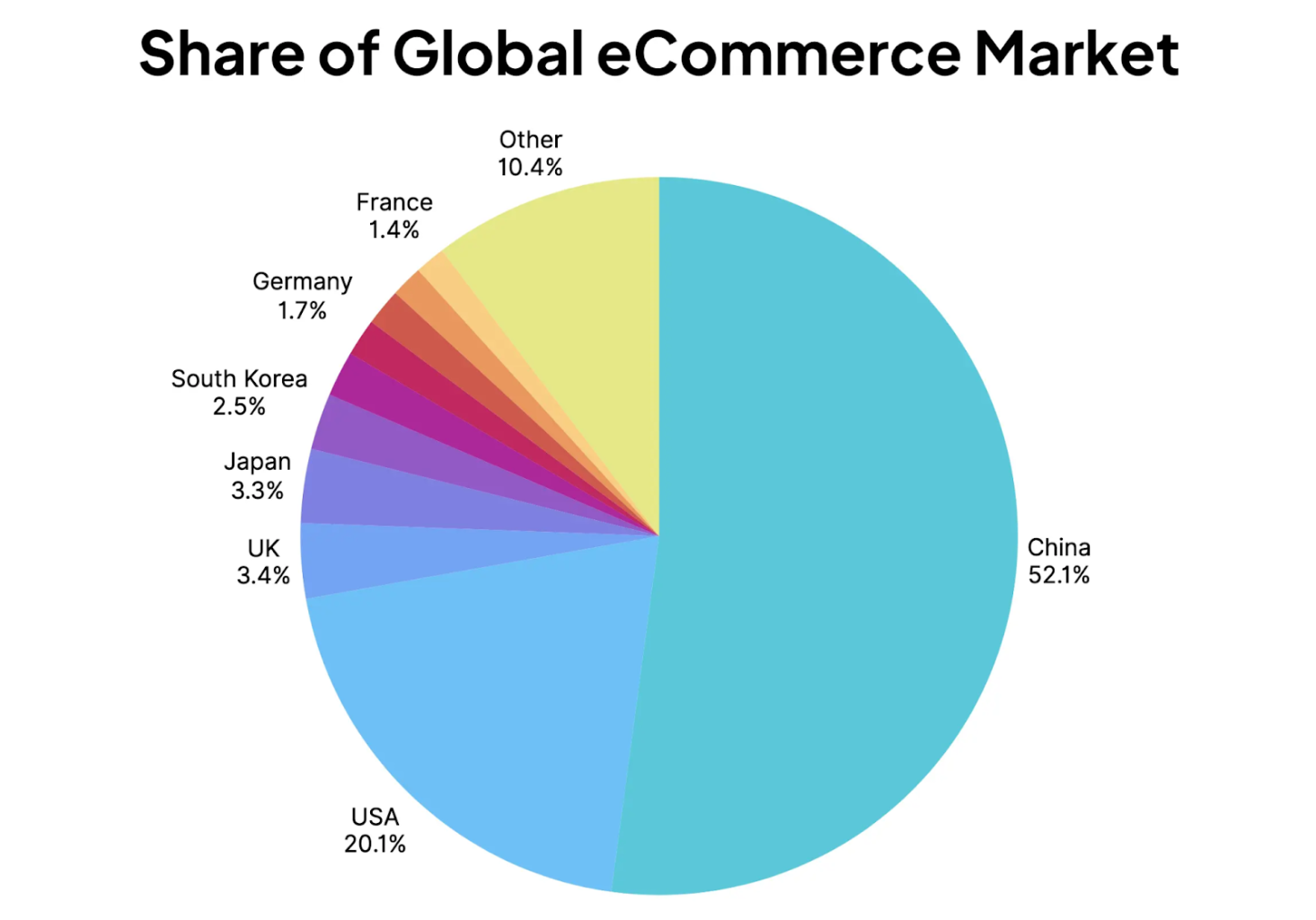
Source: Mobiloud, eCommerceDB
As you can see from Figure 2, North America and Europe also represent significant portions of the global market, with substantial growth even in maturing markets driven by technological advancements and an increasing number of consumers turning to online platforms for their shopping needs.
A better way to shop
E-commerce has been growing rapidly all over the world for several reasons. Here are some key factors contributing to its growth and popularity among consumers:
Convenience: One of the primary reasons consumers are drawn to e-commerce is the convenience it offers. Online shopping allows people to browse and purchase products or services from the comfort of their homes or virtually anywhere with an internet connection. It eliminates the need to travel to physical stores, saving time and effort.
Wide product selection: E-commerce platforms often provide a vast range of products and services in one place, offering consumers a wider selection than traditional brick-and-mortar stores. This variety allows shoppers to find items that may not be readily available locally.
Competitive pricing: E-commerce platforms often have lower overhead costs compared to physical stores, enabling them to offer competitive prices. Additionally, online retailers frequently provide discounts, deals, and promotions to attract customers. Consumers appreciate the cost savings and the ability to compare prices across different platforms.
Accessibility: E-commerce breaks down geographical barriers, allowing consumers to access products and services from anywhere in the world. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for people living in remote areas or those with limited mobility. Online shopping also provides 24/7 availability, allowing customers to make purchases at their convenience, irrespective of traditional store hours.
Personalisation and recommendation systems: E-commerce platforms employ sophisticated algorithms to analyse customer data and provide personal recommendations. By understanding consumers' preferences and purchase history, these systems can suggest relevant products, enhancing the overall shopping experience. This personalisation creates a sense of tailored service and can lead to increased customer satisfaction.
Seamless payment and delivery: E-commerce platforms offer various secure payment methods, such as credit cards, digital wallets, or even cash on delivery. Additionally, advancements in logistics and shipping services have improved delivery times, making it more convenient for consumers to receive their purchases promptly.
Given the above factors, it is unsurprising that e-commerce penetration has grown steadily all over the world. After all, who does not like convenience, a wider selection, cheaper prices, accessibility to goods from all over the world, personalisation and a seamless delivery?
E-commerce is an attractive industry
The e-commerce industry offers several compelling advantages and in our opinion, the leading businesses in this field represent attractive investment opportunities. Here are the reasons why we have invested our capital in the dominant e-commerce platforms and the related services providers:
Two-sided network effects: The dominant e-commerce platforms (marketplaces) benefit from two-sided network effects i.e. more buyers on the platform attract more sellers, and the presence of more sellers attracts more buyers. This creates a competitive advantage and makes it difficult for new players to enter the market.
Robust growth potential: The e-commerce sector has experienced strong growth rates, significantly outpacing traditional retail sectors. As digital infrastructure continues to improve and global internet penetration increases, e-commerce is set to expand even further. This sustained growth offers investors opportunities for substantial returns.
Scalability: E-commerce businesses often have high scalability potential. With the right infrastructure and technology in place, they can handle increasing sales volumes without significant proportional increases in costs. This scalability allows for efficient growth and potential for high returns on investment.
Global reach: E-commerce transcends geographical boundaries, enabling businesses to reach customers worldwide. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar stores limited by physical locations, e-commerce businesses can tap into a global customer base, expanding their market opportunities.
Lower costs: E-commerce businesses generally have lower overhead costs compared to physical stores. With reduced expenses related to rent, utilities, and in-store staffing, e-commerce operations can achieve higher profit margins.
Data and analytics: E-commerce businesses generate vast amounts of data, providing valuable insights into consumer behaviour, preferences and market trends. By leveraging data analytics, e-commerce companies can make data-driven decisions and optimise their strategies for better customer targeting and marketing. This data-driven approach enhances operational efficiency and creates a competitive advantage.
Diverse revenue streams: E-commerce businesses often have diverse revenue streams beyond traditional product sales. They can generate additional income through services like subscriptions, advertising, commissions, affiliate partnerships, payments and logistics. This diversification reduces reliance on a single revenue source and enhances the overall financial stability of the business.
Frequent, repeat purchases: E-commerce businesses that focus on building strong customer relationships are sticky and benefit from frequent, repeat purchases and customer loyalty. Businesses with loyal customers who buy frequently can provide stability of cash flows.
Agility: E-commerce businesses deal directly with their customers, therefore they can quickly respond to market trends, consumer demands, and changing industry dynamics. This flexibility allows e-commerce companies to pivot, introduce new products or services, and stay ahead of the competition.
Given the factors highlighted above, it is unsurprising that the dominant e-commerce businesses all over the world have prospered and handsomely rewarded their shareholders. Companies such as Amazon, Alibaba, Booking.com, eBay, Flipkart, JD.com and Yandex have become household names and many other lesser known businesses in the e-commerce industry have also flourished!
Sizing the opportunity
The total addressable market (TAM) for e-commerce is vast and continues to expand significantly as more of the world's shopping habits shift online. According to research firm Mordor Intelligence, the value of the global e-commerce market is set to more than double over the next five years to US$18.8 trillion, representing a compound annual growth rate of 15.8%.
As you can see from Figure 3, global e-commerce currently accounts for 20% of total retail sales and the penetration rate is expected to rise to 23% by 2027.
In China, e-commerce currently accounts for 28% of total retail sales and in the US, online shopping represents only 16% of total retail sales. Interestingly, the penetration rates in the developing regions of Asia and South America currently stand in the high single digits and these markets are growing at a much faster pace compared to their more mature counterparts.
The dominant e-commerce platforms such as Amazon, Alibaba, eBay and JD.Com have now become mature, consequently their growth rates have slowed down. Interestingly, a select few e-ecommerce platforms and services providers are still growing at a blistering pace and they appear to be attractive investment opportunities.
Figure 3: E-commerce penetration rate is rising
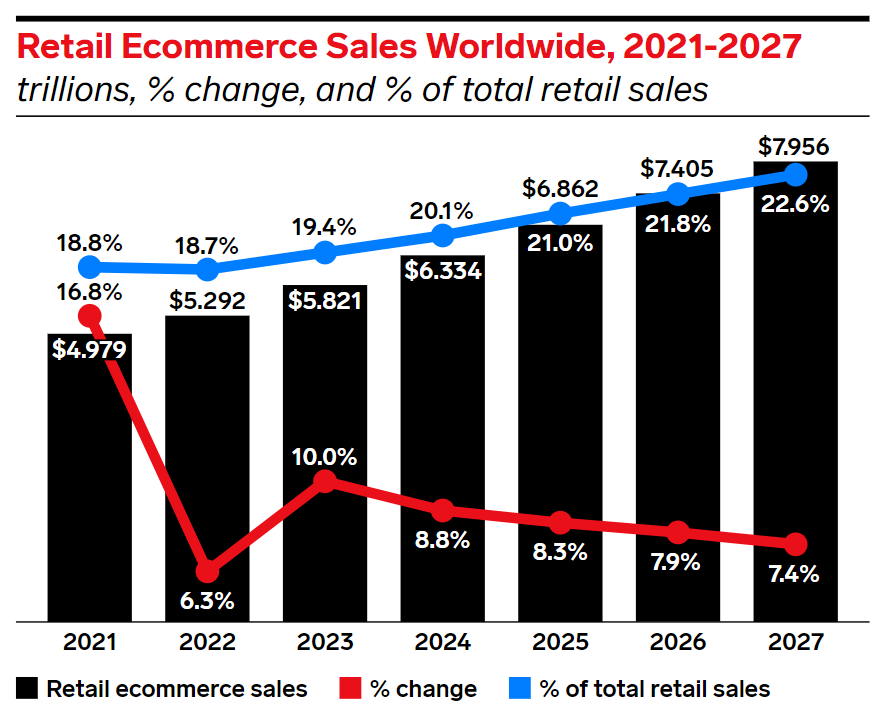
Source: eMarketer
As technology advances further and Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality become more integrated into our lives, online shopping experiences will only get better and this should benefit e-commerce businesses.
At AlphaTarget, we invest our capital in some of the most promising disruptive businesses at the forefront of secular trends; and utilise stage analysis and other technical tools to continuously monitor our holdings and manage our investment portfolio. AlphaTarget produces cutting-edge research and those who subscribe to our research service gain exclusive access to information such as the holdings in our investment portfolio, our in-depth fundamental and technical analysis of each company, our portfolio management moves and details of our proprietary systematic trend following hedging strategy to reduce portfolio drawdowns. To learn more about our research service, please visit subscriptions.




