The robotics industry encompasses the design, development, production, and application of robots across various sectors, with applications ranging from manufacturing and healthcare to entertainment and exploration. Robots are programmable machines capable of carrying out tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously, typically with precision and efficiency that extends beyond human capabilities.
This research piece aims to explore the current state, trends, and future potential growth of the robotics market so investors can better understand this nascent, long-term opportunity.
Though the world generally thinks of robots as primarily hardware, robotics does not necessarily require a hardware component; software robots have become more commonplace in recent years – most prominently including solutions such as automated chatbots and robotic process automation (RPA) platforms – enabled by recent rapid advancements in computing power and artificial intelligence.
The robotics industry is rapidly evolving with major technological advancements, including developments in artificial intelligence, machine learning, sensors, actuators, and materials science. These innovations are driving the creation of more intelligent, agile, and versatile robots capable of adapting to more dynamic environments and performing increasingly complex tasks both in the digital and physical worlds. As the capabilities of robots continue to evolve, their applications across industries should only expand, ushering in new opportunities and challenges for businesses, workers, investors, and society as a whole.
Current state of the industry
In manufacturing, industrial robots from companies such as Japan-based Fanuc and Sweden’s ABB already play crucial roles in automating repetitive tasks such as assembly, welding, painting, and material handling. These robots increase productivity, improve product quality, and enhance workplace safety by taking on hazardous or physically demanding tasks.
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are a newer development in the industry, designed to work alongside humans in shared workspaces, offering flexibility and adaptability in production lines.
One key example of cobots are warehouse robots in the logistics space, which have played a key part in bolstering productivity and streamlining inventory management, order fulfilment, and automated delivery in the e-commerce industry. Amazon.com was an early leader in this space, acquiring warehouse automation specialist Kiva Systems for US$775 million in 2012 and subsequently rolling out its warehouse-navigating bots across its vast network of fulfilment centres.
In healthcare, robots are revolutionising patient care and medical procedures. Surgical robots developed by Intuitive Surgical, Medtronic and Stryker have assisted surgeons in performing millions of minimally invasive surgeries with greater precision and control, leading to reduced patient trauma, faster recovery times, and improved surgical outcomes. Robots also aid in tasks such as medication dispensing, patient monitoring, and rehabilitation therapy, helping healthcare professionals deliver more efficient and personalised care.
Beyond manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, robots are improving sectors such as agriculture, retail, and defence. In agriculture, autonomous drones and robotic harvesters are transforming crop management and harvesting processes, increasing efficiency and yields. In defence, robots from companies including Lockheed Martin, AeroVironment, Textron, and RTX are deployed for surveillance, reconnaissance, bomb disposal, and other hazardous missions, keeping human personnel out of harm's way.
Market size, revenue share, and recent growth rates
The global robotics industry will generate revenue of more than US$40 billion in 2024, according to Statista, with the vast majority still concentrated in medical and industrial applications. The industry overall served a total addressable market (TAM) worth more than US$80 billion in 2023, having grown at a more than 10% annual clip for the past several years.
Figure 1: Robotics industry revenue share by industry
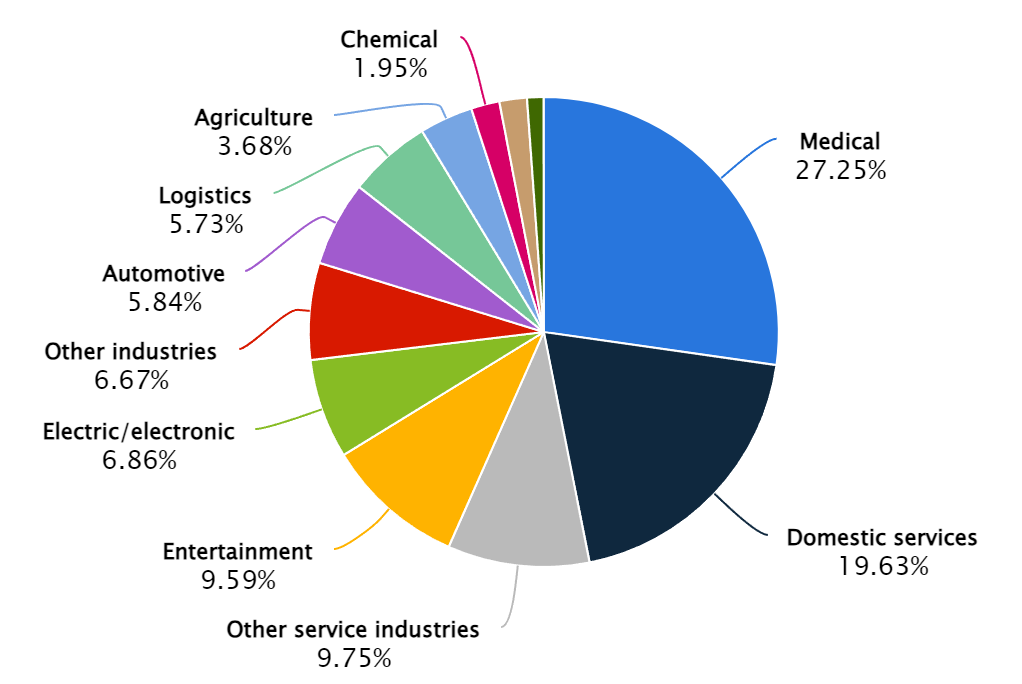
Source: Statista
Much of the industry’s recent growth, however – as well as most of its projected future growth (more on that below) – has come from professional services robots.
It was hardly surprising to that end, then, when Amazon attempted to acquire home robotics company iRobot in 2022 – a move that would have bolstered its robotics repertoire in the smart home and services segments – before the deal was ultimately scuttled by antitrust regulators in early 2024.
The case for robotics
Investing in robotics offers numerous advantages, from boosting efficiency to fostering innovation, which makes it a critical focus for future-oriented businesses and industries. Here are some of the key tailwinds that make investing in robotics a compelling option:
- 1. Increased productivity and efficiency: Robotics technology significantly enhances productivity in manufacturing and service sectors by performing tasks faster and with greater precision than human workers. Robots can operate continuously without breaks, which maximises output and efficiency and they do not become ill or require annual leave.
- 2. Cost reduction: Over time, the use of robotics can lead to substantial cost savings. Robots reduce labour costs, minimise errors, and decrease waste. Additionally, predictive maintenance capabilities of modern robots can prevent costly downtime for a wide variety of both robotic and non-robotic platforms alike, anticipating and addressing potential mechanical issues before they become problematic.
- 3. Safety and ergonomics: Robotics can tackle dangerous or hazardous tasks that pose undue risks to human workers. This not only reduces the likelihood of workplace injuries but also improves the overall working conditions.
- 4. Innovation and competitive advantages: The deployment of robotics technology drives innovation by introducing new capabilities and enabling businesses to explore new product lines and markets. Companies that adopt robotics can gain a significant competitive edge, as they are often seen as leaders in technological adoption.
- 5. Addressing labour shortages: In many industries, there is a growing gap between the availability of skilled labour and the requirements of modern production processes. Robots can fill this gap, especially in regions or sectors experiencing labour shortages, ensuring that production levels and growth targets are met.
Investing in robotics is not just about automating tasks; it's about transforming business operations to be more efficient, safe, and innovative. This transformation is crucial as industries evolve and the global market becomes more competitive. By embracing robotics, companies can better position themselves for future growth and success. And investors can benefit from this success by putting their capital to work accordingly.
Key developments and trends
At present, the industrial sector is primarily using robots in manufacturing to enhance productivity and efficiency. The integration of incrementally advanced AI in recent years has allowed these robots to perform increasingly complex tasks such as predictive maintenance and quality control, further driving their adoption. The professional services sector, which includes logistics, healthcare, and hospitality, is also seeing increased utilisation of robots for tasks like transportation, cleaning, and personal assistance.
The robotics industry is experiencing dynamic growth and accelerating innovation, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), collaborative robots (cobots), and service robotics.
At the time of writing (May 2024), the key trends shaping the robotics sector include:
- 1. Artificial intelligence integration: AI continues to be a major driver in the robotics industry, enhancing robot capabilities in autonomy, predictive maintenance, and interaction. AI enables robots to handle complex tasks and environments by improving their decision-making and efficiency
- 2. Growth of collaborative robots (Cobots): Cobots are designed to work alongside humans in a shared workspace, enhancing safety and efficiency. They are increasingly being used across various industries, including automotive and electronics, due to their adaptability and ease of integration.
- 3. Expansion of service robotics: Service robots are being deployed across a wide range of non-industrial sectors such as healthcare, logistics, and hospitality. These robots perform tasks ranging from transportation and logistics support to personal assistance and healthcare services, reflecting a growing diversification in robot applications.
- 4. Improving dexterity and digital twins: Innovations like mobile manipulators combine mobility with manipulative abilities, enabling robots to perform material handling and maintenance tasks more efficiently. Additionally, digital twin technology is being used to optimise robot operations through virtual simulations, which predict performance outcomes and maintenance needs. Autonomous vehicle designers are actively using digital twin technology, for instance, to explore new designs and sensor combinations as well as improving reaction times.
- 5. Humanoid robots and Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS): Humanoid robots are being developed to operate in environments designed for humans, performing a range of tasks from warehouse operations to customer service. Meanwhile, RaaS models are also gaining traction, allowing companies the ability to deploy robotics without massive upfront investments in R&D and hardware, further lowering the barrier to automation adoption.
Sizing the opportunity
The robotics market is expected to grow rapidly over the next several years (Figure 2). According to research firm Boston Consulting Group, the market for robotics is expected to grow from approximately US$40 billion in 2024 to US$160-$260 billion by 2030. This represents an annual compounded growth rate of 26-37% over the next 6 years!
Figure 2: The robots are coming
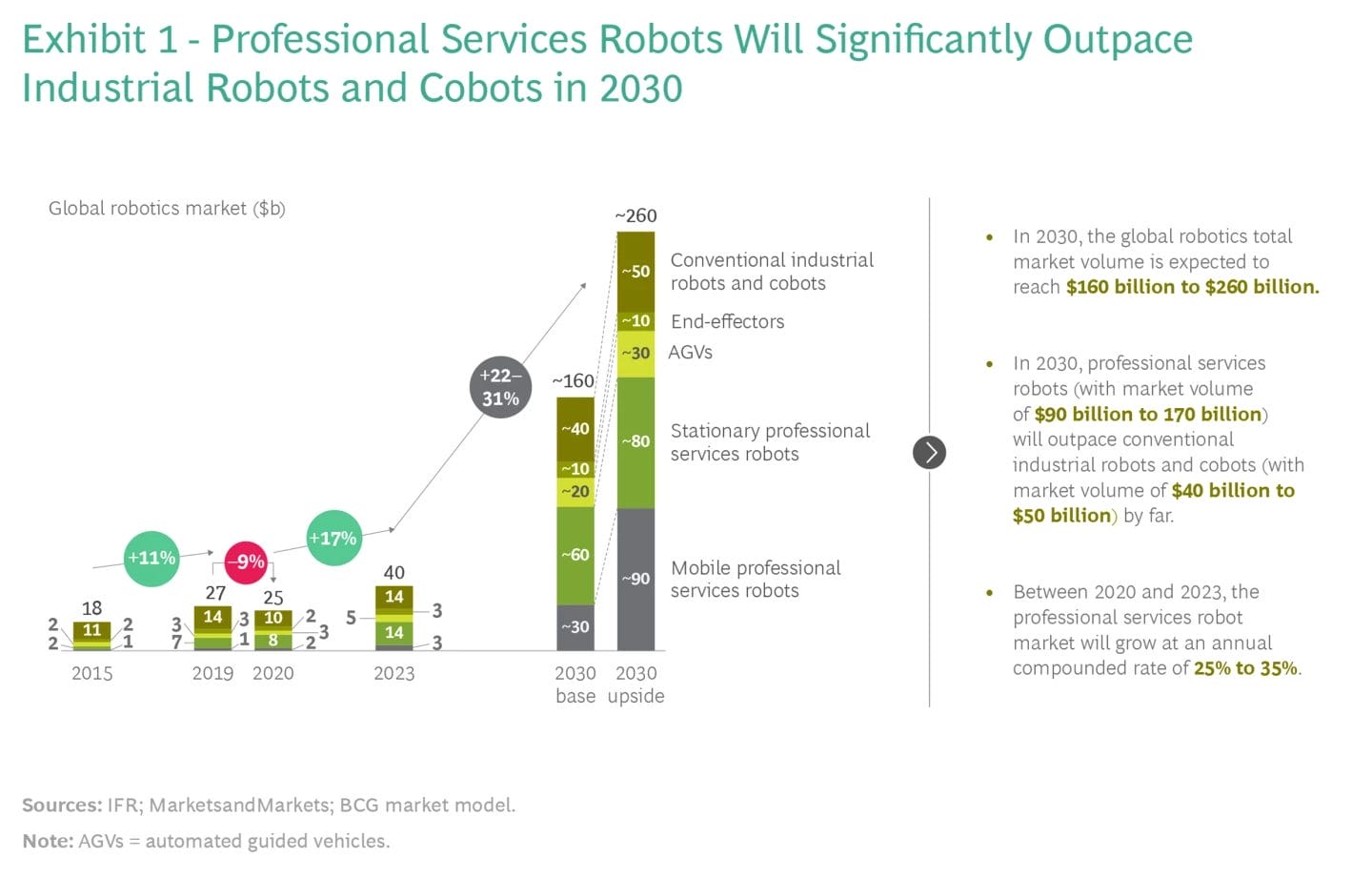
Source: Boston Consulting Group
A substantial portion of this growth is likely to come from professional services robots, which could generate twice as much revenue as conventional and logistics robots.
The collaborative robots (cobots) segment alone is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.7% from 2022 to 2030 – to just under US$8 billion – indicating strong demand for robots that can safely complement the work of human partners.
Given that the total addressable market (TAM) for the robotics industry is expected to grow exponentially, it is worth considering which specific sub-sectors might represent the most promising investment opportunities.
Our research suggests that humanoid robots are arguably the most exciting growth opportunity for their combination of high-tech novelty and immense potential growth. According to research from Goldman Sachs, the global humanoid TAM could reach an estimated US$38 billion by 2035 and this projection assumes that 1.4 million units are being sold annually a decade from today. Initial humanoid robot applications will likely focus on industrial and manufacturing operations, before gradually transitioning to other industries including hospitality and personal care.
We expect Tesla and Hyundai Motor subsidiary Boston Dynamics to stand tall as leaders in humanoid robotics development in the coming years.
Various “Robots as a Service” (RAAS) offerings should also enjoy outsized growth, recurring revenues and high margins. Symbotic is one notable leader to that end, having recently teamed up with SoftBank to offer a compelling AI-based warehouse-as-a-service platform in the logistics space.
Tesla also has the potential to benefit greatly on the RAAS front through its planned robotaxi ride hailing service as well as its Optimus humanoid robot. The electric vehicle leader only recently offered consumers the first glimpse of its robotaxi app in April 2024 and Elon Musk is of the view that ultimately, Tesla’s Optimus business will become the company’s biggest business division.
Apart from Tesla and Boston Dynamics, a number of start-ups in the private markets in China, Europe and the US have also developed humanoid robots and given the size of the industry, some of these companies are likely to reward their shareholders.
At AlphaTarget, we invest our capital in some of the most promising disruptive businesses at the forefront of secular trends; and utilise stage analysis and other technical tools to continuously monitor our holdings and manage our investment portfolio. AlphaTarget produces cutting-edge research and those who subscribe to our research service gain exclusive access to information such as the holdings in our investment portfolio, our in-depth fundamental and technical analysis of each company, our portfolio management moves and details of our proprietary systematic trend following hedging strategy to reduce portfolio drawdowns. To learn more about our research service, please visit subscriptions.